Ever wondered why you feel sluggish, irritable, or just not yourself? Well, it might have something to do with chronic inflammation and hormone imbalance. In this blog, we're diving into the impact of chronic inflammation on hormone imbalance. From the causes of chronic inflammation to the sneaky symptoms of hormone imbalance, we'll break it all […]

Ever wondered why you feel sluggish, irritable, or just not yourself? Well, it might have something to do with chronic inflammation and hormone imbalance.
In this blog, we're diving into the impact of chronic inflammation on hormone imbalance. From the causes of chronic inflammation to the sneaky symptoms of hormone imbalance, we'll break it all down for you. So, let's unravel the mystery of how these two factors are intertwined and what you can do to restore balance for a happier, healthier you!
Chronic inflammation is a prolonged and persistent inflammatory response in the body, characterized by an overactive immune system that continuously releases inflammatory compounds. Unlike acute inflammation, which is a short-term and beneficial response to injury or infection, chronic inflammation can persist for weeks, months, or even years, leading to tissue damage and dysfunction.
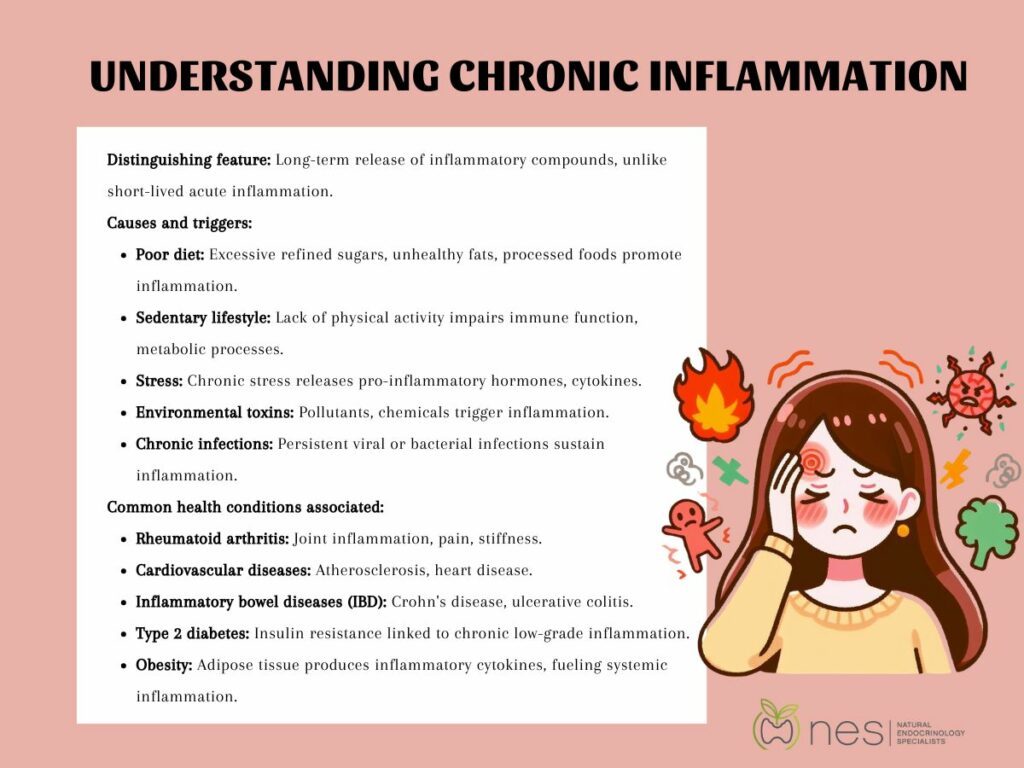
Causes and triggers of chronic inflammation are multifaceted and can stem from various factors, including:
Common health conditions associated with chronic inflammation include:
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by various glands in the endocrine system, regulating numerous physiological processes such as metabolism, growth and development, reproduction, and mood. Hormone balance is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being, as even minor fluctuations can lead to significant disruptions in bodily functions.
Factors that can lead to hormone imbalance include:
Symptoms of hormone imbalance vary depending on the specific hormones involved and may include:
Chronic inflammation and hormone imbalance are intricately connected, with one often exacerbating the other. Here's how chronic inflammation can disrupt hormone production and regulation and the impact on specific hormones on their relationship:
Chronic inflammation induces changes in the body's regulatory mechanisms, impacting hormone production and signaling pathways. One significant way inflammation affects hormones is through the dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which controls the release of stress hormones like cortisol. Prolonged inflammation can lead to HPA axis dysfunction, resulting in abnormal cortisol levels and impaired stress response.
Inflammatory cytokines released during chronic inflammation can interfere with the function of hormone-secreting glands such as the thyroid, pancreas, and adrenal glands. This interference disrupts the synthesis, secretion, and action of hormones involved in metabolism, immune function, and stress response. Below are the impact of Inflammation on specific hormones:
Prolonged hormone imbalance resulting from chronic inflammation can have significant health consequences, exacerbating inflammation and perpetuating a vicious cycle of dysfunction. Here's a closer look at the effects of hormone imbalance caused by chronic inflammation:
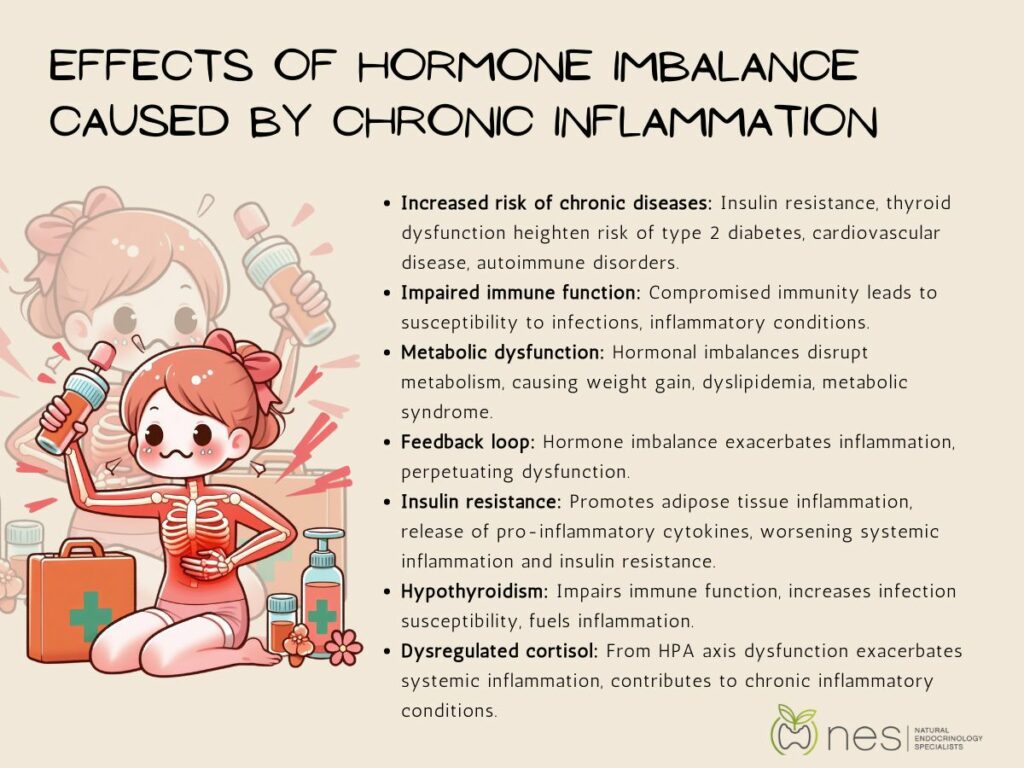
Hormone imbalance can further exacerbate inflammation, creating a feedback loop that perpetuates dysfunction. For example, insulin resistance promotes adipose tissue inflammation and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, exacerbating systemic inflammation and insulin resistance.
Additionally, hormonal imbalances such as hypothyroidism can impair immune function and increase susceptibility to infections, further fueling inflammation. Likewise, dysregulated cortisol levels resulting from HPA axis dysfunction can exacerbate systemic inflammation and contribute to chronic inflammatory conditions.
Chronic inflammation is closely linked with disruptions in hormone balance, which can affect overall health and well-being. Managing this inflammation through lifestyle changes, dietary recommendations, and stress management techniques is essential for restoring and maintaining hormone balance.
Lifestyle adjustments are pivotal in reducing chronic inflammation. Regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to combat inflammation.
Diet plays a crucial role in managing inflammation and supporting hormone health. Anti-inflammatory diets emphasize the intake of whole foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, whole grains, and fatty fish like salmon and mackerel. These foods contain vital nutrients that help reduce inflammatory processes and support the production and regulation of hormones.
Incorporating healthy fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, is also beneficial. These can be found in flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Omega-3s are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and their role in producing hormones. Avoiding processed foods, sugars, and trans fats is equally important, as these can increase inflammation and disrupt hormonal balance.
Chronic stress is a significant contributor to chronic inflammation and hormonal imbalances. Effective stress management is, therefore, essential for maintaining hormonal equilibrium and overall health.
And there you have it, folks! Chronic inflammation and hormone imbalance might sound like complicated medical jargon, but understanding their connection is crucial for your well-being. By making simple lifestyle changes, embracing a balanced diet, and managing stress effectively, you can take charge of your health and restore harmony in your body. So, remember to listen to your body, prioritize self-care, and take proactive steps toward achieving optimal health.

Acupuncture Session - $189.00
Acupuncture, Package of 4 - $636.00
Female Pellet Insertion Package - $518.00
Male Pellet Insertion Package - $744.00